Objects Introduction
Objects are custom data models that define the structure of your business data in Monetize360. Create Objects to store and manage your data with fields, relationships, and validation rules.
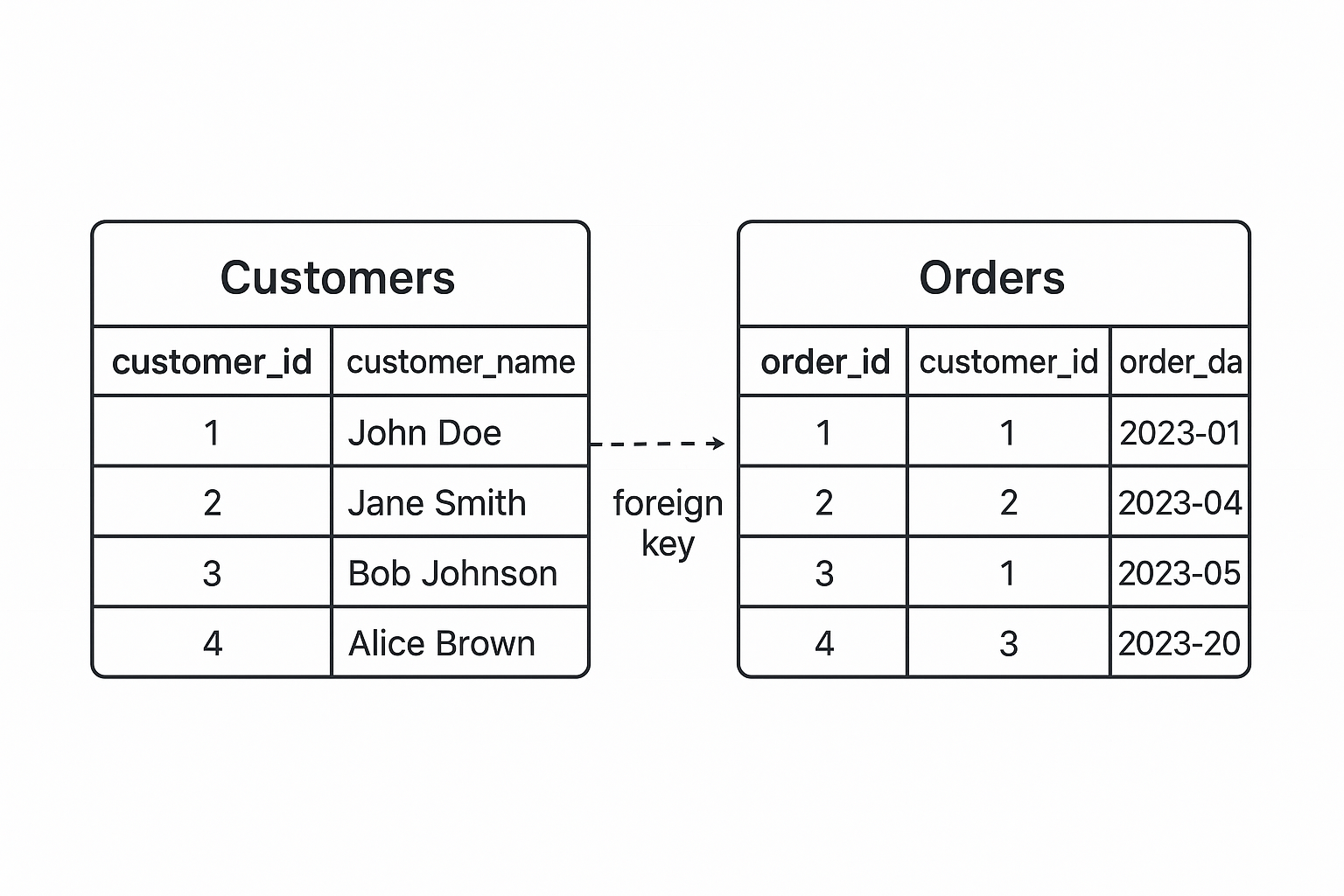
What are Objects?
Objects define your data structure. Think of an Object as a table or database schema that defines the structure for storing related data. Each Object contains:
- Fields with specific data types (text, number, date, etc.)
- Lookup fields (foreign keys) for relationships between objects
- Picklist fields for dropdown values
- Validation rules
- Audit trails (optional)
Auto-Created Resources
When you create an Object, the system automatically creates:
-
Workflows: Standard CRUD workflows are automatically generated:
- Save Flow: Create new records
- Edit Flow: Update existing records
- Delete Flow: Delete records
- Import Flow: Import data from files
- Export Flow: Export data to files
- Excel Import Flow: Import data from Excel/CSV files
-
DataGrid: A default datagrid is automatically created with:
- All Object fields displayed as columns
- Pre-configured actions (Save, Edit, Delete, Import, Export, Excel Import)
- Ready-to-use interface for viewing and managing Data records
These auto-created resources are organized in directories matching your Object name, making it easy to find and customize them as needed.
Key Concepts
Fields
Define fields to store your data:
- Text: Names, descriptions, notes
- Number: Quantities, prices, amounts
- Date: Dates and timestamps
- Boolean: True/false values
- Lookup: Links to other Objects (creates relationships)
- Picklist: Predefined dropdown options
Relationships
Create relationships between Objects using Lookup fields:
- Link customers to orders
- Link products to categories
- Link invoices with payments
Data
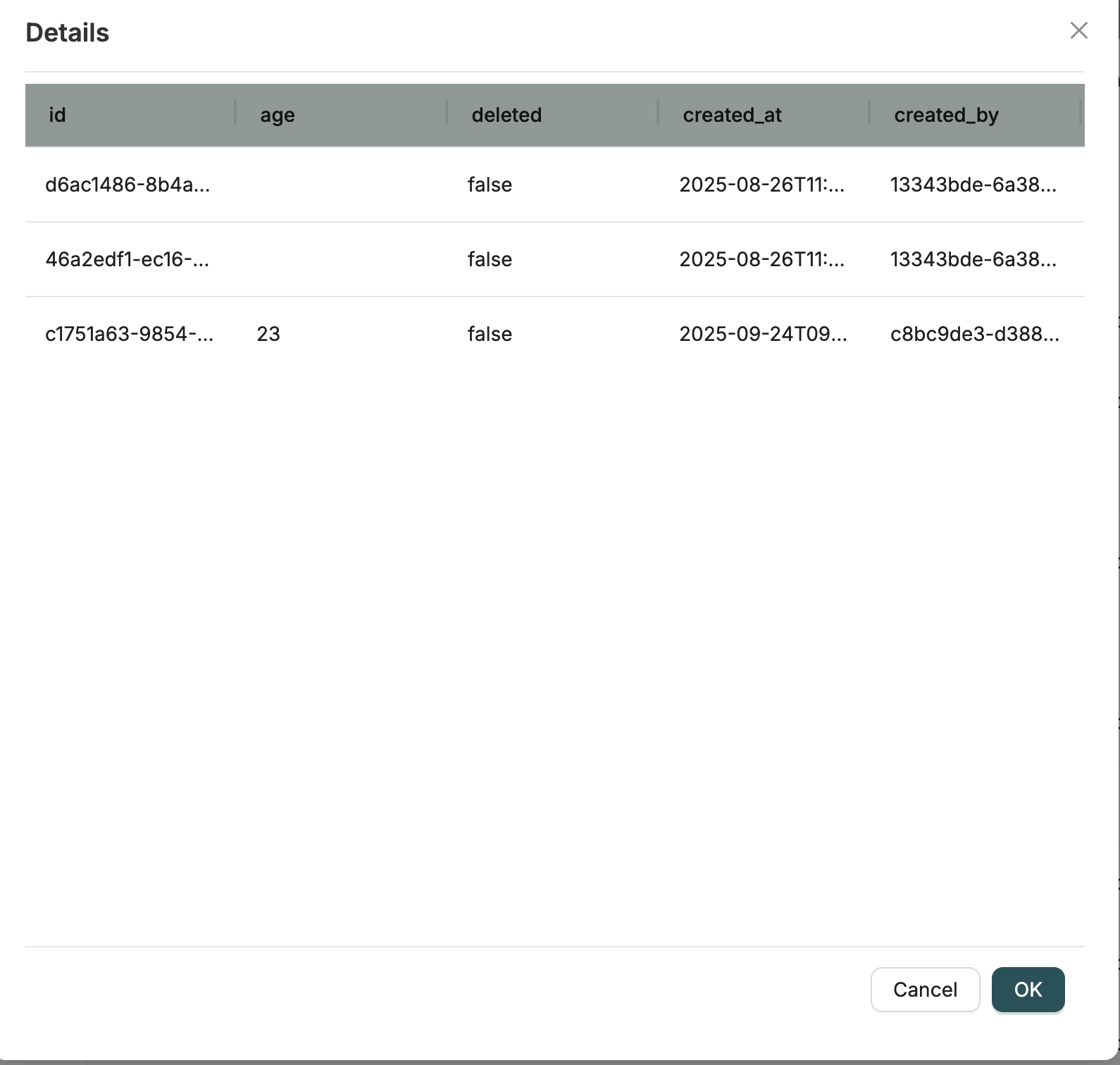
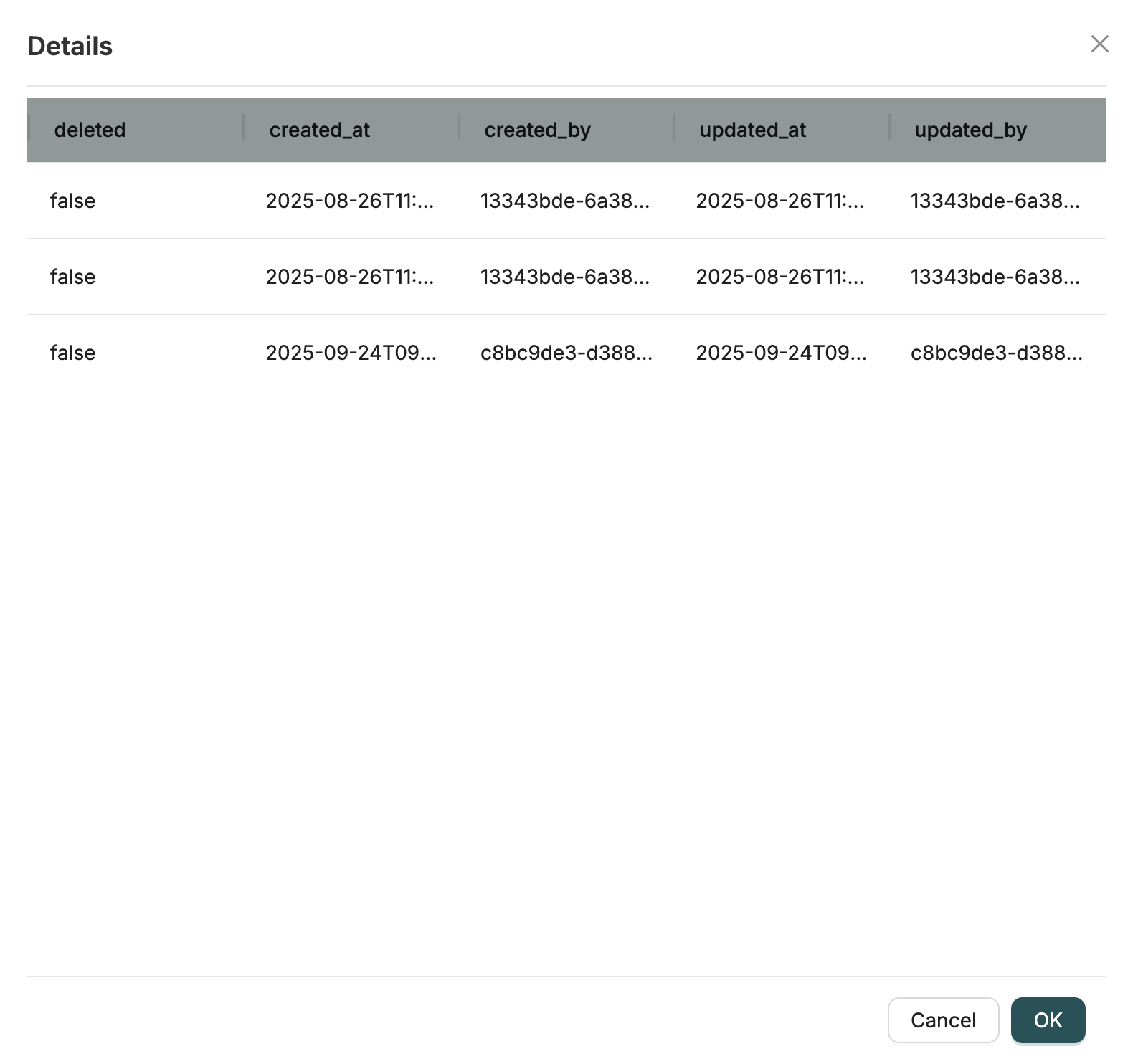
Data represents the actual data records stored within your Objects. While Objects define the structure (schema), Data contains the actual instances of that data.
- Object: The blueprint or template (e.g., "Customer" schema with fields like name, email, address)
- Data: The actual records conforming to that blueprint (e.g., individual customer records with real values)
Each Data record is a JSON document that follows the schema defined by its parent Object. Data records include:
- Business data fields (as defined in the Object schema)
- System properties (id, created_at, created_by, updated_at, updated_by, deleted)
Data Management
Once you've created Objects, use CRUD operations to manage your data:
Getting Started
- Create an Object: Learn how to create Objects and configure their settings
- Add Fields: Learn about all available field types and their use cases
- Add Data: Create or update records in your Objects
Related Introduction
- Schema Builder - Understanding the Schema Builder interface for defining fields
- Creating Objects - Learn how to create Objects and configure their settings
- Field Types - Complete reference for all field types
- CRUD Operations - Work with Object data
- Getting Started - Build your first workflow